Concepts
Concepts around ksctl core
This section will help you to learn about the underlying system of Ksctl. It will help you to obtain a deeper understanding of how Ksctl works.
📐 Architecture
Here is the entire Ksctl system level design

Sequence diagrams for 2 major operations
Create Cloud-Managed Clusters
sequenceDiagram
participant cm as Manager Cluster Managed
participant cc as Provision Controller
cm->>cc: transfers specs from user or machine
cc->>cc: to create the cloud infra (network, subnet, firewall, cluster)
cc->>cm: 'kubeconfig' and other cluster access to the state
cc->>cm: status of creationCreate Self-Managed HA clusters
sequenceDiagram
participant csm as Manager Cluster Self-Managed
participant cc as Provision Controller
participant bc as Bootstrap Controller
csm->>cc: transfers specs from user or machine
cc->>cc: to create the cloud infra (network, subnet, firewall, vms)
cc->>csm: return state to be used by BootstrapController
csm->>bc: transfers infra state like ssh key, pub IPs, etc
bc->>bc: bootstrap the infra by either (k3s or kubeadm)
bc->>csm: 'kubeconfig' and other cluster access to the state
bc->>csm: status of creation1 - Cluster Summary and Recommendation
Documentation on Ksctl’s cluster summary and recommendation features
Cluster Summary and Recommendation
Ksctl provides you a comprehensive summary of your cluster’s configuration and provides both:
- debugging information in entire cluster scope
- recommendation in terms of security
Note
This feature is available in Ksctl v2.7+.
Please note this command will work out of the box for any cluster created by ksctl v2.X+
Also Note this Operation is Read heavy make sure you run this command when you are not doing any heavy operations on the cluster.
Here is the demo on how it looks
Why Cluster Summary?
It will give users access to the important details of their cluster with just a single command $ ksctl cluster summary
It will help users with the following:
- Debugging: It will help users to debug their cluster in a single command. From:
- Errors in Pods failing,
- metrics from server to know directly what is wrong with the cluster.
- Cluster Events
- Latency: It gives you report of what is the latency between you and the cluster
- Recommendation: It gives remediation of problems it finds in the cluster. We are currently looking for these problems as of now:
- PodSecurityPolicy: It will check if the PodSecurityPolicy is enabled or not. If not, it will give a recommendation to enable it.
- NamespaceQuota: It will check if the NamespaceQuota is enabled or not. If not, it will give a recommendation to enable it.
- PodResourceLimits & Requests: It will check if the PodResourceLimits & Requests are enabled or not. If not, it will give a recommendation to enable it.
- NodePort: It will check if the NodePort is enabled or not. If not, it will give a recommendation to remove them.
How to use it?
This subcommand got introduced in Ksctl v2.7. You can use it by running the following command for any existing cluster:
2 - Smart Cost & Emission Optimization
Documentation on Ksctl’s intelligent region and instance selection features
Smart Cost & Emission Optimization
Ksctl provides intelligent optimization features that help you minimize infrastructure costs and environmental impact when deploying Kubernetes clusters. These features ensure that your clusters run in both the most cost-effective and environmentally friendly configurations.
Ksctl Optimizer (KO) (v2.4+)
Introduced in Ksctl v2.4, KO optimizes costs and emissions by intelligently selecting the most efficient region for your Kubernetes clusters without changing your instance type.
Key Benefits
- 🚀 Automatic Region Optimization: Ksctl intelligently identifies and switches to the most cost-effective and environmentally friendly regions.
- 🛠️ Flexible Region Control: You can opt to keep your cluster in your preferred region if needed.
- 💰 Cost Savings: Dynamically adapts to pricing changes across regions, reducing your infrastructure expenses.
- 🌱 Eco-Friendly Operations: Minimizes carbon footprint through smart region selection.
How It Works
It evaluates regions based on multiple metrics to determine the optimal location for your Kubernetes clusters:
- Direct Carbon Intensity (Lower is better): Measures the carbon emissions from energy production.
- LCA Carbon Intensity (Lower is better): Evaluates the lifecycle carbon emissions of energy sources.
- Renewable Power Percentage (Higher is better): Highlights regions with higher renewable energy usage.
- Low CO₂ Power Percentage (Higher is better): Focuses on regions with a lower share of carbon-intensive power.
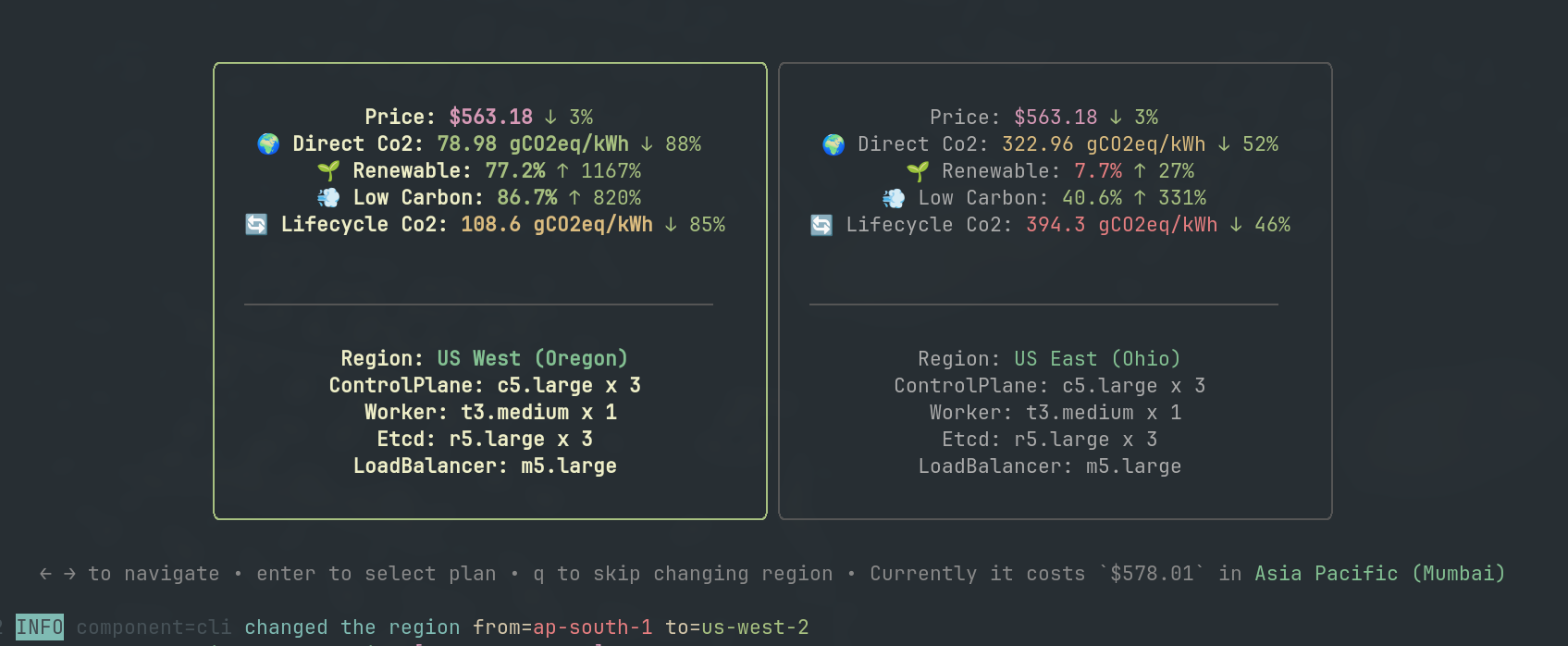 Visualization of dynamic region switching optimization
Visualization of dynamic region switching optimization
Ksctl Sustainability Metrics (KSM) (v2.5+)
Introduced in Ksctl v2.5, this feature enhances the optimization capabilities through a card-based selection interface that helps you choose the best region and instance type for your Kubernetes clusters based on your specific requirements.
Smart Region Selection
This feature ranks regions based on emission optimization metrics, ensuring that your Kubernetes clusters are not only cost-effective but also environmentally friendly.
Key Benefits
- 🌱 Minimizes carbon footprint by prioritizing regions with lower emissions.
- 🚀 Automatically ranks regions using advanced emission metrics.
How It Works
The Smart Region Selection evaluates and ranks regions based on the same comprehensive emission metrics used in Dynamic Region Switching:
- Direct Carbon Intensity
- LCA Carbon Intensity
- Renewable Power Percentage
- Low CO₂ Power Percentage
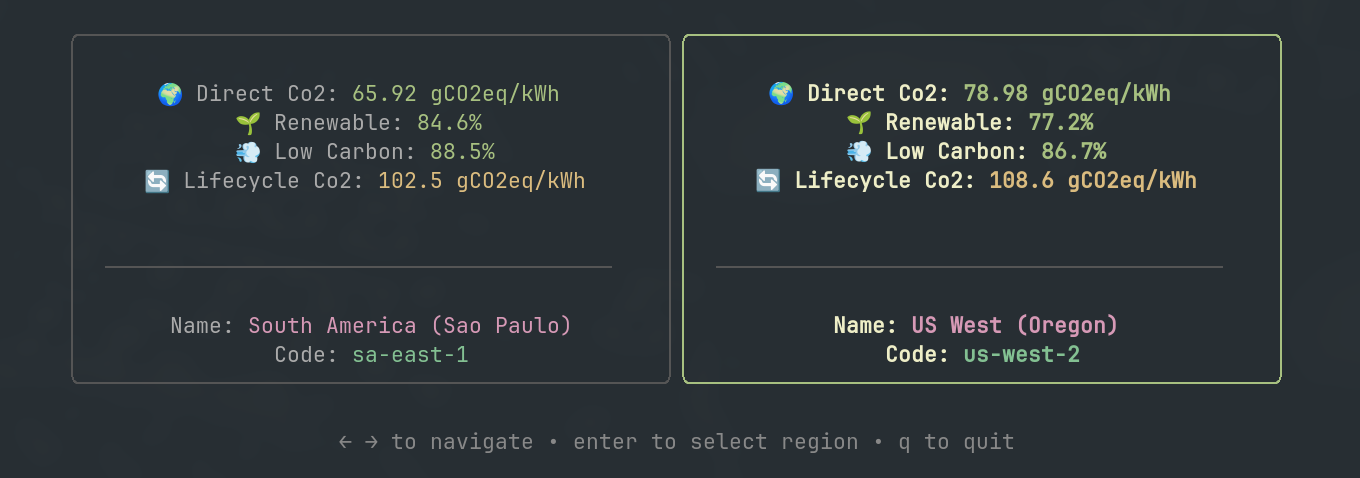 Visualization of region selection optimization based on emission metrics
Visualization of region selection optimization based on emission metrics
Smart Instance Type Selection
This feature helps you choose the most efficient instance type based on both cost and embodied emissions, ensuring that your Kubernetes clusters are optimized for efficiency and sustainability.
Key Benefits
- 💰 Cost Optimization: Adapts to pricing changes across instance types to reduce infrastructure costs.
- 🌱 Sustainability Focus: Prioritizes instance types with lower embodied emissions, minimizing your carbon footprint.
How It Works
The Smart Instance Type Selection evaluates and ranks instance types based on:
- Cost Efficiency: Analyzes and compares pricing across different instance types.
- Embodied Emissions: Evaluates the environmental impact of manufacturing and deploying each instance type.
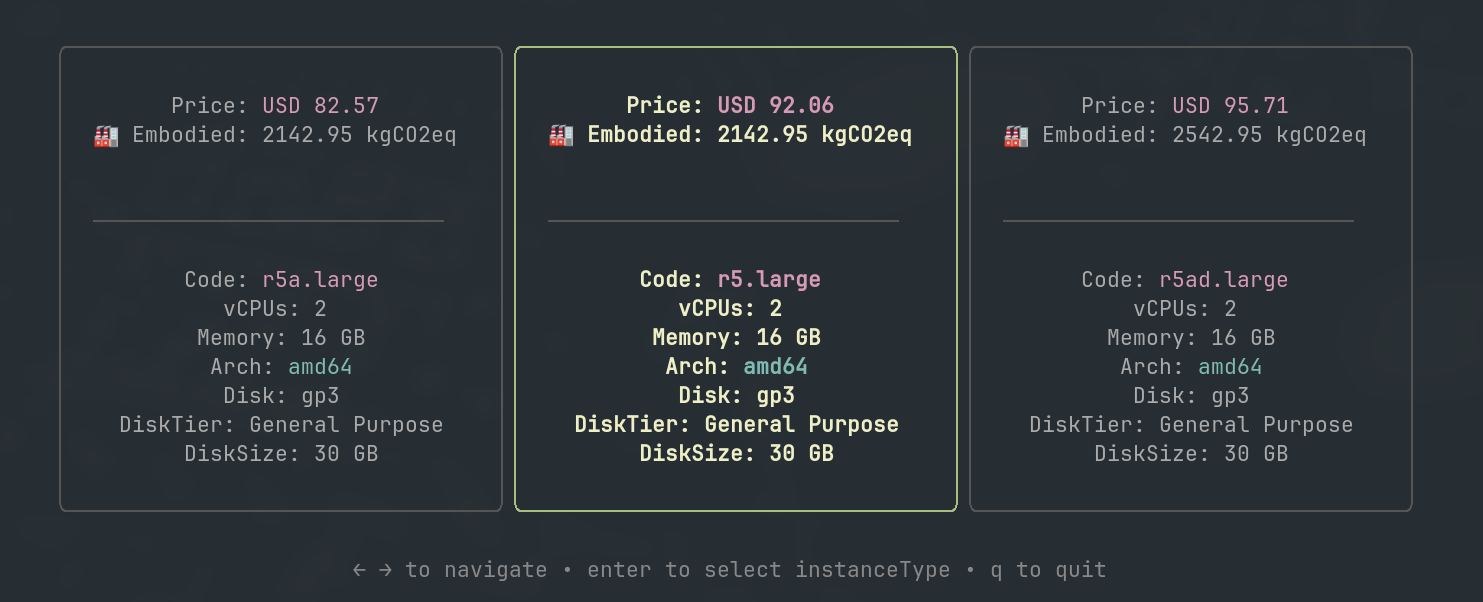 Visualization of instance type selection optimization based on cost and embodied emissions
Visualization of instance type selection optimization based on cost and embodied emissions
Using the Optimization Features
These optimization features are integrated with the ksctl cluster create command and work automatically when you create a new Kubernetes cluster.
When you run the cluster creation command, Ksctl will:
- Analyze available regions and instance types
- Evaluate cost and emission metrics for each option
- Present optimized recommendations through an intuitive interface
- Allow you to select the best options for your specific needs
This ensures you get maximum cost efficiency and minimum emissions while maintaining performance and reliability for all your Kubernetes deployments.
Upgrading to Access These Features
To access these optimization features, make sure you’re using Ksctl v2.4 or above by running:
This will ensure you have the latest version with all the optimization capabilities described in this document.
3 - Cloud Controller
The Component of Ksctl responsible for creating and managing clusters for different Cloud platforms.
It is responsible for controlling the sequence of tasks for every cloud provider to be executed
4 - Core functionalities
How does the core functionalities of ksctl work
Basic cluster operations
Create
- HA self-managed cluster (VM is provisioned and ssh into and configure them just like ansible)
- Managed (cloud provider creates the clusters and we get the kubeconfig in return)
Delete
- HA self managed cluster
- Managed cluster
Scaleup
- Only for ha cluster as the user has manual ability to increase the number of worknodes
- Example: if workernode 1 then it will create 2 then 3…
Scaledown
- Only for ha cluster as the user has manual ability to decrease the number of worknodes
- Example: if workernodes are 1, 2 then it will delete from the last to first aka 2 then 1
Switch
- It will just use the request from the user to get the kubeconfig from specific cluster and save to specific folder that is ~/.ksctl/kubeconfig
Get
- Both ha and manage cluster it will search folders in specific directory to get what all cluster have been created for specific provider
Example:
Here for get request of azure it will scan the directory .ksctl/state/azure/ha and for managed as well to get all the folder names

5 - Core Manager
The Component of Ksctl responsible for managing Cloud controller and Distribution controller. It has multiple types of managers
It is responsible for managing client requests and calls the corresponding controller
Types
ManagerClusterKsctl
Role: Perform ksctl getCluster, switchCluster
ManagerClusterKubernetes
Role: Perform ksctl addApplicationAndCrds
Currently to be used by machine to machine not by ksctl cli
ManagerClusterManaged
Role: Perform ksctl createCluster, deleteCluster
ManagerClusterSelfManaged
Role: Perform ksctl createCluster, deleteCluster, addWorkerNodes, delWorkerNodes
6 - Distribution Controller
The Component of Ksctl responsible for selecting the type of Bootstrap solution (Kubeadm or K3s).
It is responsible for controlling the execution sequence for configuring Cloud Resources wrt to the Kubernetes distribution choosen

 Visualization of dynamic region switching optimization
Visualization of dynamic region switching optimization Visualization of region selection optimization based on emission metrics
Visualization of region selection optimization based on emission metrics Visualization of instance type selection optimization based on cost and embodied emissions
Visualization of instance type selection optimization based on cost and embodied emissions